您好!歡迎訪問洛陽富道生物科技有限公司官方網(wǎng)站!

Programmed cell death 1 (PD‐1) and its ligands PD‐L1 and PD‐L2 are receptors that act in co‐stimulatory and coinhibitory immune responses. Signaling the PD‐1/PD‐L1 or PD‐L2 pathway isessential to regulate the inflammatory responses to infections, autoimmunity, and allergies, and it has been extensively studied in cancer. Allergic diseases include asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis, atopic dermatitis, drug allergy, and anaphylaxis. These overactive immune responses involveIgE‐dependent activation and increased CD4+ T helper type 2 (Th2) lymphocytes. Recent studies have shown that PD‐L1 and PD‐L2 act to regulate T‐cell activation and function. However, the main role of PD‐1 and its ligands is to balance the immune response; however, the inflammatory process of allergic diseases is poorly understood. These immune checkpoint molecules can function as a brake or a kick‐start to regulate the adaptive immune response. These findings suggest that PD‐1 and its ligands may be a key factor in studying the exaggerated response in hypersensitivity reactions in allergies. This review summarizes the current understanding of the role of PD‐1 and PD‐L1 and PD‐L2 pathway regulation in allergic diseases and how this immunomodulatory pathway is currently being targeted to develop novel therapeutic immunotherapy.
程序性細(xì)胞死亡 1 (PD-1) 及其配體 PD-L1 和 PD-L2 是在共刺激和共抑制免疫反應(yīng)中起作用的受體。向 PD-1/PD-L1 或 PD-L2 通路發(fā)出信號(hào)對(duì)于調(diào)節(jié)對(duì)感染、自身免疫和過敏的炎癥反應(yīng)至關(guān)重要,它已在癌癥中得到廣泛研究。過敏性疾病包括哮喘、鼻結(jié)膜炎、特應(yīng)性皮炎、藥物過敏和過敏反應(yīng)。這些過度活躍的免疫反應(yīng)涉及 IgE 依賴性激活和 CD4+ T 輔助 2 型 (Th2) 淋巴細(xì)胞增加。最近的研究表明,PD-L1 和 PD-L2 可調(diào)節(jié) T 細(xì)胞的激活和功能。然而,PD-1及其配體的主要作用是平衡免疫反應(yīng);然而,人們對(duì)過敏性疾病的炎癥過程知之甚少。這些免疫檢查點(diǎn)分子可以起到剎車或啟動(dòng)的作用,以調(diào)節(jié)適應(yīng)性免疫反應(yīng)。這些發(fā)現(xiàn)表明,PD-1 及其配體可能是研究過敏癥中超敏反應(yīng)過度反應(yīng)的關(guān)鍵因素。本綜述總結(jié)了目前對(duì) PD-1 和 PD-L1 以及 PD-L2 通路調(diào)節(jié)在過敏性疾病中的作用的理解,以及目前如何針對(duì)這種免疫調(diào)節(jié)通路開發(fā)新型治療性免疫療法。
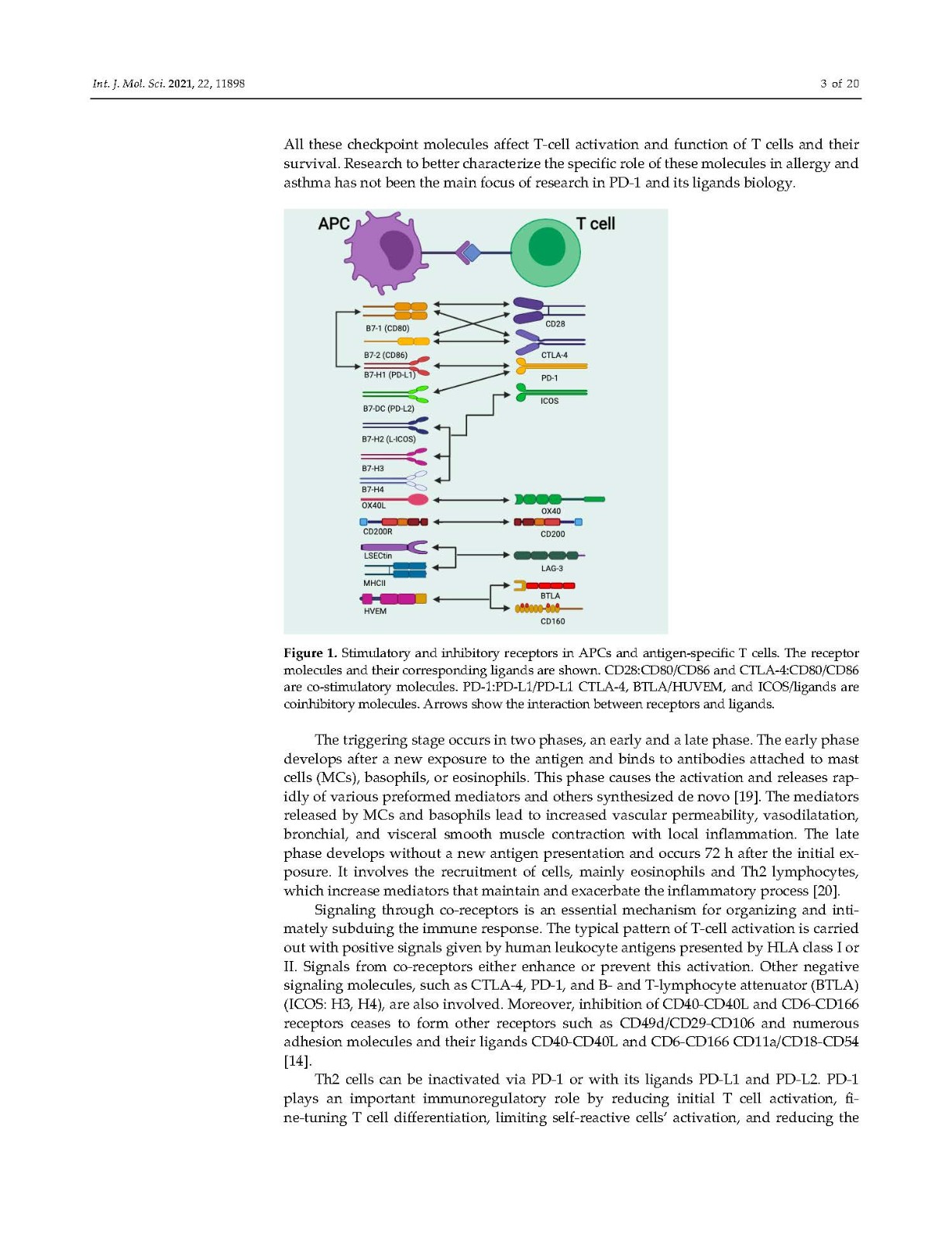
CD4+ T cells require three complementary signals to become fully activated—the T‐cell receptor (TCR) signal, co‐stimulation/inhibition signals, and cytokine priming. The first signal confers specificity to the immune response and plays an essential role in rec‐ognizing antigen presentation by MHC‐II on the surface of APCs. However, this signal alone is not sufficient to fully activate these T cells. For full efficacy, T cells need a second,non‐specific co‐stimulatory signal. The coupling between APCs and naive T cells will signal surface molecules expressed on T cells and APCs. Both express co‐stimulatory molecules such as CD80 and CD86, which belong to the B7 family. These molecular in‐teractions modulate T cell function by binding to CD28 or cytotoxic T‐lymphocyte‐associated antigen 4 (CTLA‐4) receptors; this interaction has been ob‐served to have opposing effects depending on the different environmental signals.CTLA‐4 inhibits T‐cell responses and regulates peripheral T‐cell tolerance. At the sametime, CD28 promotes T‐cell activation and survival. Finally, cytokines control differenti‐ation into different effector cells that deliver signals such as IL‐4, IL‐5, IL‐13, INFs, and proinflammatory cytokines [1]. This finding shows that these immunological checkpoint molecules have a role in fine‐tuning the T‐cell response by mediating stimulatory and inhibitory signals.
CD4+ T細(xì)胞需要三種互補(bǔ)信號(hào)才能完全激活T細(xì)胞受體(TCR)信號(hào),共刺激/抑制信號(hào),細(xì)胞因子啟動(dòng)。的第一個(gè)信號(hào)賦予免疫反應(yīng)特異性,并在應(yīng)答中起重要作用通過MHC‐II識(shí)別apc表面的抗原呈遞。然而,這個(gè)信號(hào)單獨(dú)不足以完全激活這些T細(xì)胞。為了充分發(fā)揮功效,T細(xì)胞需要第二次,非地理公司應(yīng)承擔(dān)的刺激信號(hào)。apc和原始T細(xì)胞之間的結(jié)合會(huì)T細(xì)胞和APCs上表達(dá)的信號(hào)表面分子。都表達(dá)公司的刺激分子如CD80和CD86,它們屬于B7家族。這些分子的量相互作用通過結(jié)合CD28或細(xì)胞毒性來調(diào)節(jié)T細(xì)胞功能T淋巴細(xì)胞相關(guān)抗原4 (CTLA - 4)受體;這種互動(dòng)一直是ob‐根據(jù)不同的環(huán)境信號(hào),會(huì)產(chǎn)生相反的效果。CTLA - 4抑制T細(xì)胞反應(yīng)并調(diào)節(jié)外周T細(xì)胞耐受。在同一隨著時(shí)間的推移,CD28促進(jìn)T細(xì)胞的活化和存活。最后,細(xì)胞因子的控制是不同的IL - 4、IL - 5、IL - 13、inf和IL - 4等信號(hào)傳遞到不同的效應(yīng)細(xì)胞中促炎細(xì)胞因子[1]。這一發(fā)現(xiàn)表明這些免疫檢查點(diǎn)分子在通過介導(dǎo)刺激和調(diào)節(jié)T細(xì)胞反應(yīng)中起著重要作用抑制信號(hào)。

















關(guān)鍵詞 :allergy; PD‐1; PD‐L1; PD‐L2; asthma; BTLA; rhinoconjunctivitis; atopic dermatitis; food allergy; anaphylaxis
來源:MDPI https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/21/11898
上一篇: 細(xì)胞培養(yǎng)瓶使用注意這三點(diǎn)
下一篇: 血清瓶中的血清如何儲(chǔ)存