您好!歡迎訪問洛陽富道生物科技有限公司官方網(wǎng)站!

Schwann cells play a crucial role in successful peripheral nerve repair and regeneration by supporting both axonal growth and myelination. Schwann cells are therefore a feasible option for cell therapy treatment of peripheral nerve injury. However, sourcing human Schwann cells at quantities required for development beyond research is challenging. Due to their availability, rapid in vitro expansion, survival, and integration within the host tissue, stem cells have attracted considerable attention as candidate cell therapies. Among them, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) with the associated prospects for personalized treatment are a promising therapy to take the leap from bench to bedside. In this critical review, we firstly focus on the current knowledge of the Schwann cell phenotype in regard to peripheral nerve injury, including crosstalk with the immune system during peripheral nerve regeneration. Then, we review iPSC to Schwann cell derivation protocols and the results from recent in vitro and in vivo studies. We finally conclude with some prospects for the use of iPSCs in clinical settings.

40層細胞工廠
雪旺氏細胞通過支持軸突生長和髓鞘形成,在成功的周圍神經(jīng)修復和再生中發(fā)揮著至關重要的作用。因此,施萬細胞是外周神經(jīng)損傷的細胞療法治療的可行選擇。然而,以研究之外的開發(fā)所需的數(shù)量采購人類雪旺氏細胞具有挑戰(zhàn)性。由于它們的可用性、快速的體外擴增、存活和在宿主組織內的整合,干細胞作為候選細胞療法引起了相當多的關注。其中,具有相關個性化治療前景的誘導多能干細胞 (iPSCs) 是一種很有前景的療法,可以實現(xiàn)從工作臺到床邊的飛躍。在這篇批判性評論中,我們首先關注與周圍神經(jīng)損傷有關的雪旺細胞表型的當前知識,包括在周圍神經(jīng)再生過程中與免疫系統(tǒng)的串擾。然后,我們回顧了 iPSC 到 Schwann 細胞衍生協(xié)議以及最近體外和體內研究的結果。我們最后總結了在臨床環(huán)境中使用 iPSC 的一些前景。
Schwann cells play a critical role in peripheral nerve repair through axon guidance and promoting the establishment of a pro-regenerative environment in the nerve bridge. However, primary SCs may not be ideal for efficient use in cell therapies, due mainly to difficulties in purifying and a long expansion process. Despite extensive efforts to develop reliable methods to differentiate stem cells to SCs as an alternative source, both adult stem cells and ESCs have drawbacks—from low purity and yield, non-neuronal differentiation potential, and accessibility of cells, to ethical considerations. Although therapies using differentiated cells sourced from iPSCs will require extensive screening prior to use, iPSCs have the benefits of ESCs without the drawback of ethical concerns which have been cited as a potential barrier to the application of ESC therapies worldwide.

細胞轉瓶2L
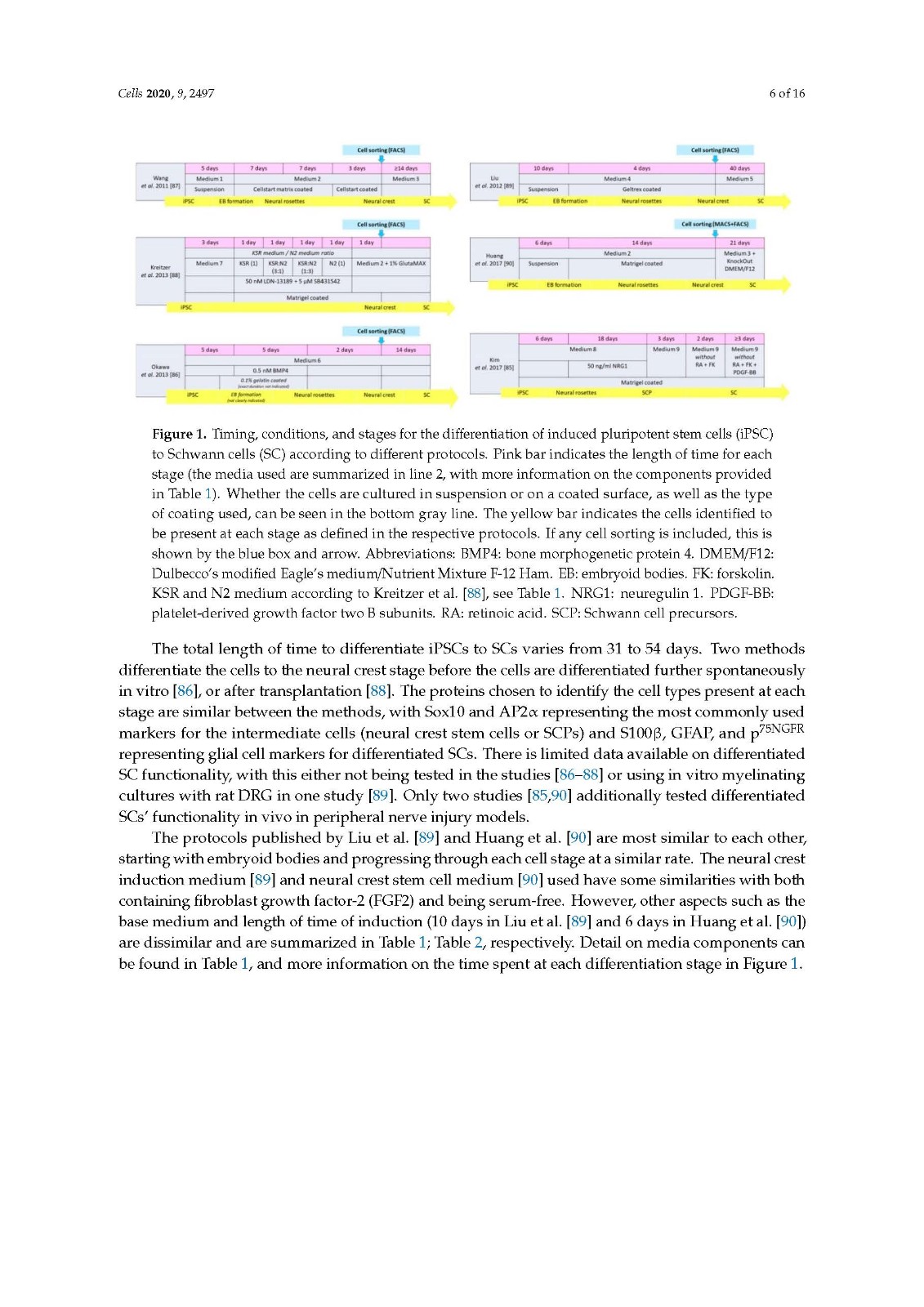
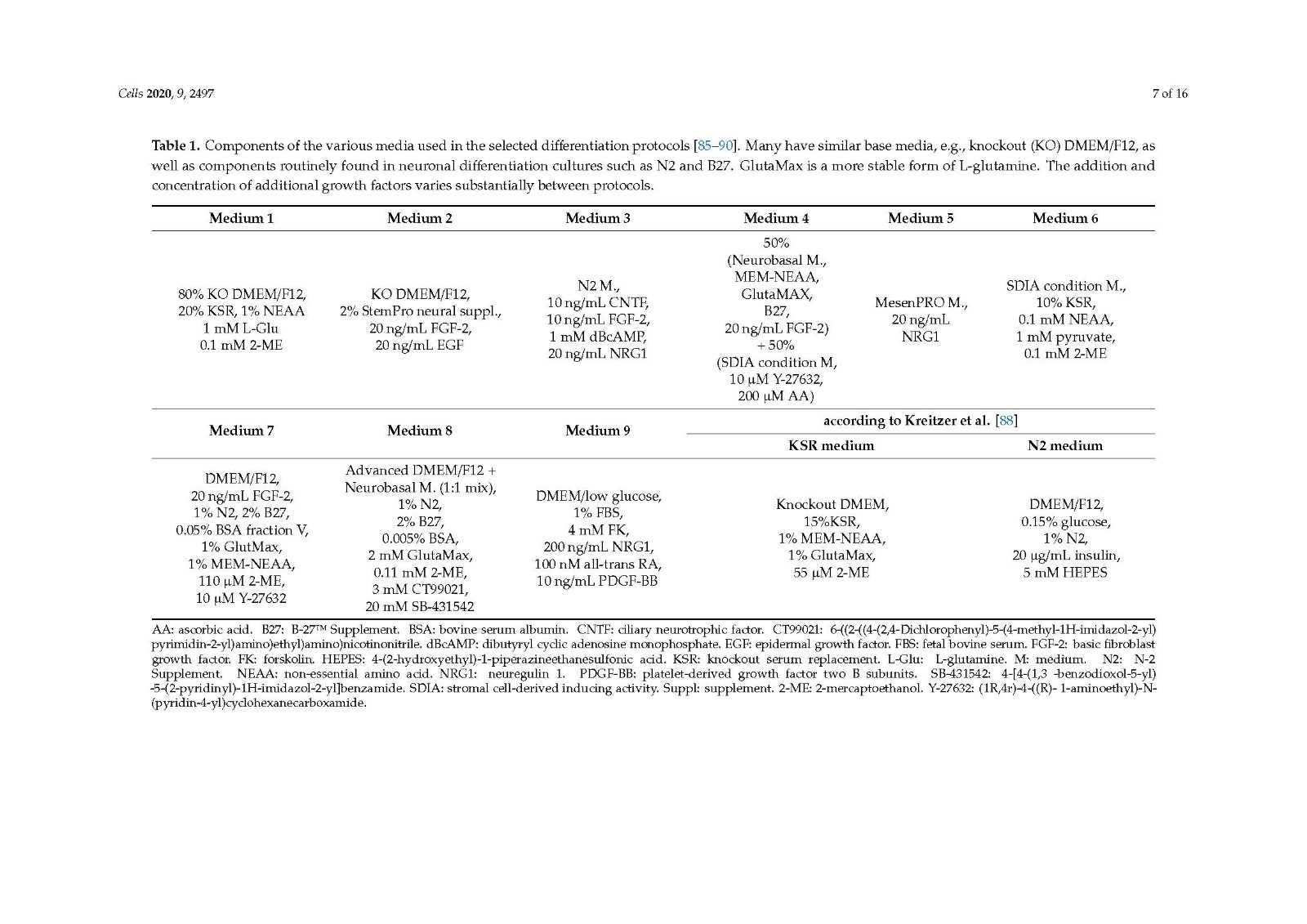
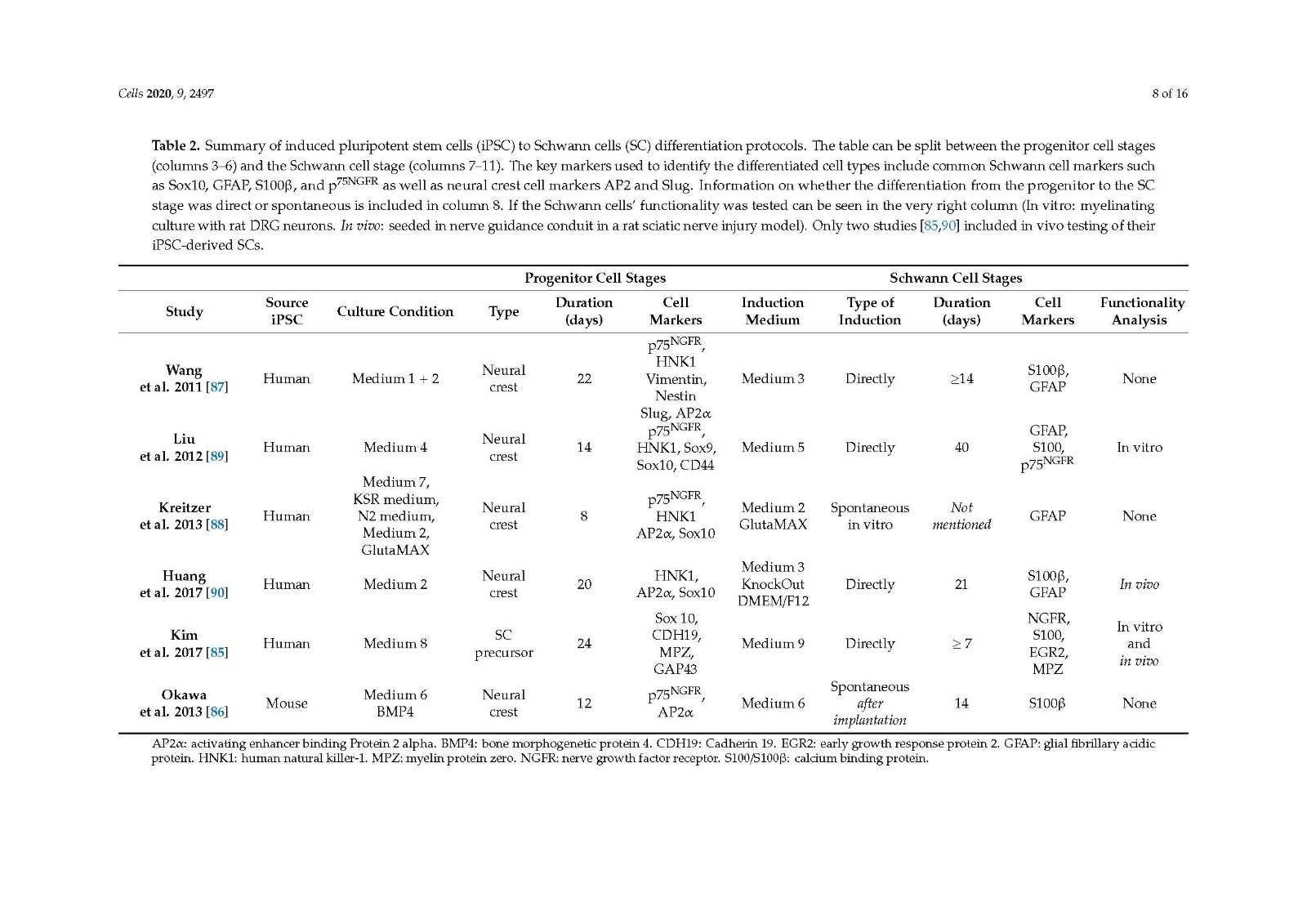
There are several protocols differentiating iPSCs to neural crest stem cells, with the three studies looked at in the current review [85,89,90] including a step to differentiate progenitor cells to SCs, showing promising outcomes both in vitro and in vivo. All three methods generate differentiated cells that express SC markers and release neurotrophic factors. A clear comparison of in vivo outcomes on peripheral nerve repair cannot be made due to the varied choice of animal models used.
It would be beneficial to compare the cell types derived from the different protocols in similar animal models of peripheral nerve injury, the true determinant being how well they perform compared to the autograft in a critical length gap and comprehensive functional analysis. Despite this, the use of iPSCs as a source for Schwann cells for use in future peripheral nerve injury repair therapies remains very promising.
雪旺氏細胞通過軸突引導和促進神經(jīng)橋中促再生環(huán)境的建立,在周圍神經(jīng)修復中發(fā)揮關鍵作用。然而,原代 SCs 可能不是有效用于細胞療法的理想選擇,主要是由于純化困難和漫長的擴增過程。盡管為開發(fā)將干細胞分化為 SCs 作為替代來源的可靠方法做出了廣泛的努力,但成體干細胞和 ESCs 都存在缺點——從低純度和產量、非神經(jīng)元分化潛力和細胞的可及性,到倫理考慮。盡管使用來自 iPSC 的分化細胞進行治療需要在使用前進行廣泛的篩選,有幾種協(xié)議分化iPSC的神經(jīng)嵴干細胞,與當前審查,包括一個步驟分化祖細胞的SC,顯示出在體外和體內有前途的結果。所有三種方法都會產生表達 SC 標志物并釋放神經(jīng)營養(yǎng)因子的分化細胞。由于使用的動物模型的選擇多種多樣,因此無法對周圍神經(jīng)修復的體內結果進行明確的比較。

高效搖瓶5L
在類似的周圍神經(jīng)損傷動物模型中比較來自不同方案的細胞類型將是有益的,真正的決定因素是它們在臨界長度間隙和綜合功能分析中與自體移植相比的表現(xiàn)如何。盡管如此,使用 iPSC 作為雪旺細胞的來源,用于未來的周圍神經(jīng)損傷修復療法仍然非常有希望。













來 源:MDPI https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/9/11/2497/htm
關鍵詞 雪旺細胞,chwann cells,induced pluripotent stem cells, peripheral nerve,regenerative medicine,誘導多能干細胞,周圍神經(jīng),再生醫(yī)學
上一篇: 為什么血清瓶要求無內毒素
下一篇: 細胞轉瓶中的細胞貼壁情況差是什么原因