您好!歡迎訪問洛陽富道生物科技有限公司官方網(wǎng)站!

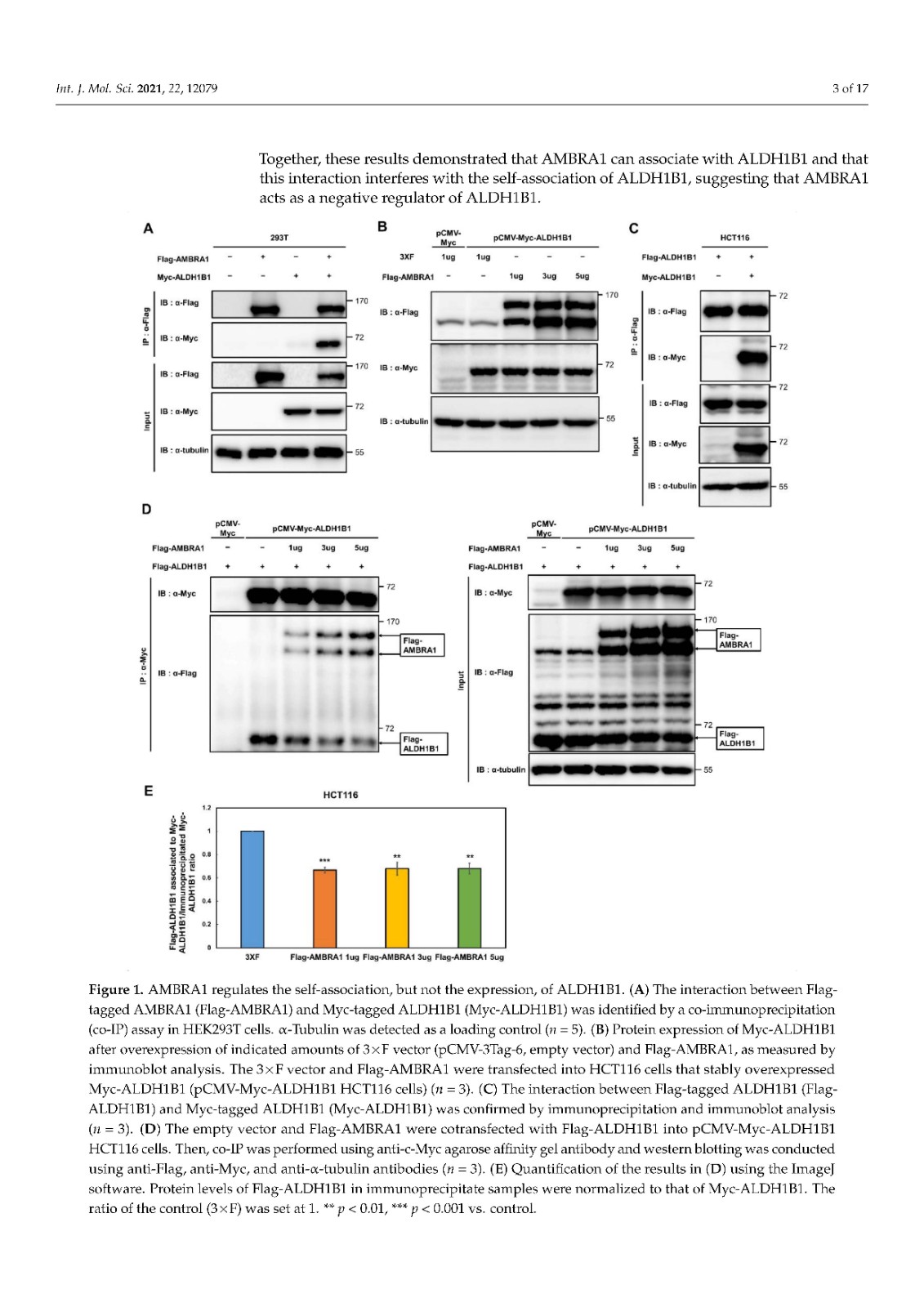
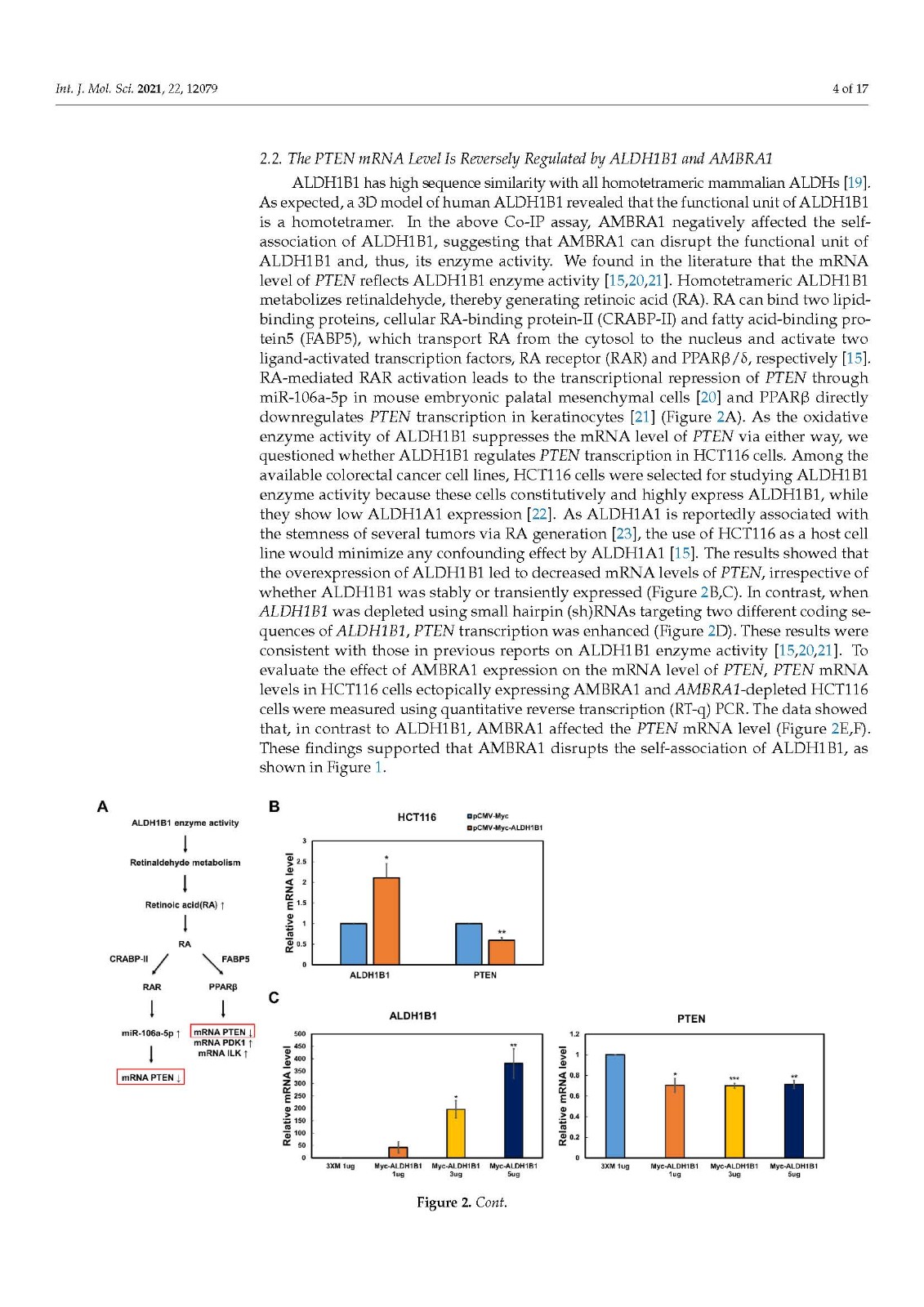
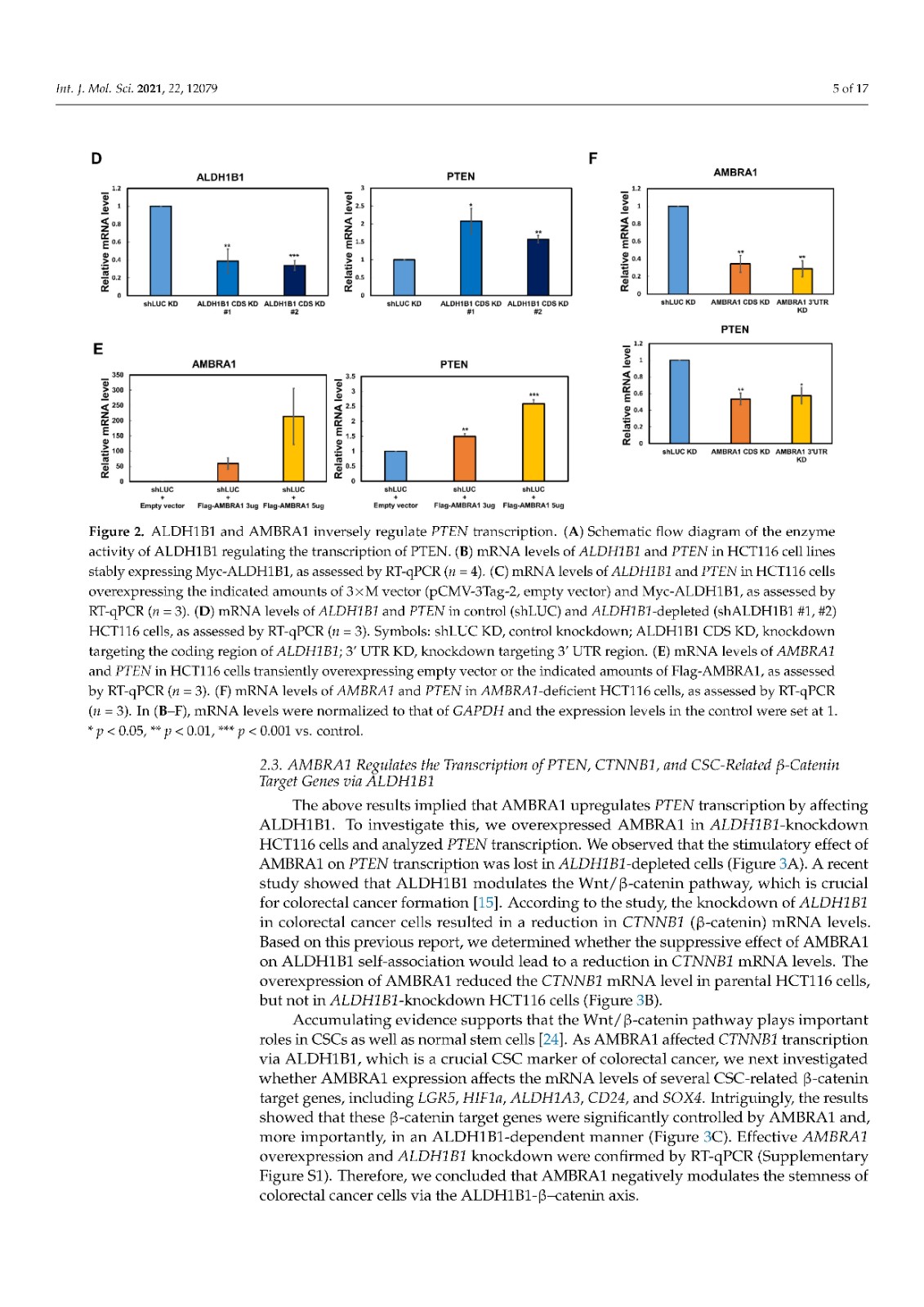
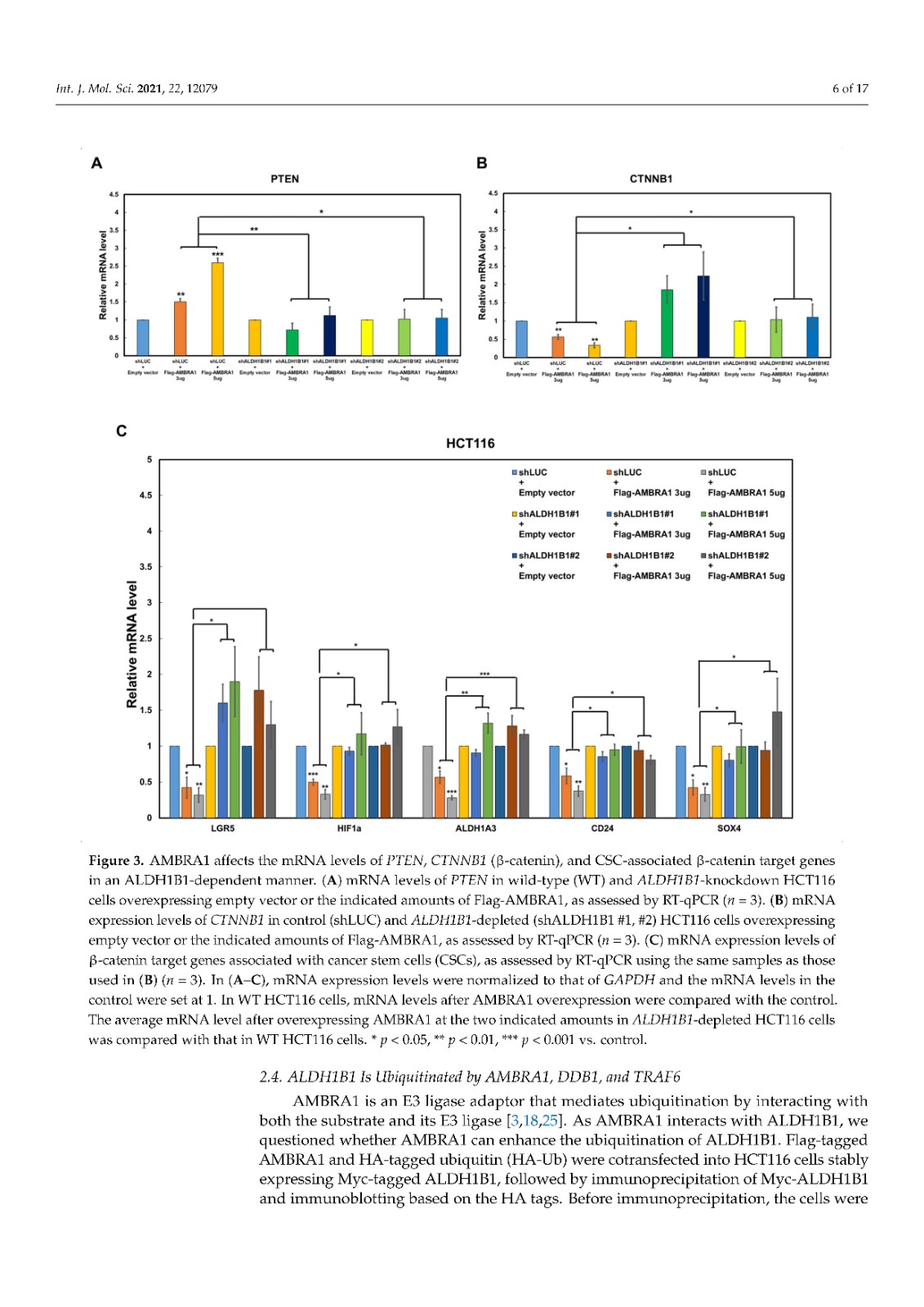
Activating molecule in Beclin-1-regulated autophagy (AMBRA1), a negative regulator of tumorigenesis, is a substrate receptor of the ubiquitin conjugation system. ALDH1B1, an aldehyde dehydrogenase, is a cancer stem cell (CSC) marker that is required for carcinogenesis via upregulation of the β-catenin pathway. Although accumulating evidence suggests a role for ubiquitination in the regulation of CSC markers, the ubiquitination-mediated regulation of ALDH1B1 has not been unraveled. While proteome analysis has suggested that AMBRA1 and ALDH1B1 can interact, their interaction has not been validated. Here, we show that AMBRA1 is a negative regulator of ALDH1B1. The expression of ALDH1B1-regulated genes, including PTEN, CTNNB1 (β-catenin), and CSC-related β-catenin target genes, is inversely regulated by AMBRA1, suggesting a negative regulatory role of AMBRA1 in the expression of ALDH1B1-regulated genes. We found that the K27- and K33-linked ubiquitination of ALDH1B1 is mediated via the cooperation of AMBRA1 with other E3 ligases, such as TRAF6. Importantly, ubiquitination site mapping revealed that K506, K511, and K515 are important for the K27-linked ubiquitination of ALDH1B1, while K33-linked ubiquitination occurs at K506. A ubiquitination-defective mutant of ALDH1B1 increased the self-association ability of ALDH1B1, suggesting a negative correlation between the ubiquitination and self-association of ALDH1B1. Together, our findings indicate that ALDH1B1 is negatively regulated by AMBRA1-mediated noncanonical ubiquitination.
Beclin-1 調(diào)節(jié)的自噬 (AMBRA1) 中的激活分子是腫瘤發(fā)生的負調(diào)節(jié)因子,是泛素結(jié)合系統(tǒng)的底物受體。ALDH1B1 是一種醛脫氫酶,是一種癌癥干細胞 (CSC) 標志物,通過上調(diào) β-catenin 途徑,是致癌作用所必需的。盡管越來越多的證據(jù)表明泛素化在 CSC 標志物調(diào)控中的作用,但泛素化介導的 ALDH1B1 調(diào)控尚未解開。雖然蛋白質(zhì)組分析表明 AMBRA1 和 ALDH1B1 可以相互作用,但它們的相互作用尚未得到驗證。在這里,我們表明 AMBRA1 是 ALDH1B1 的負調(diào)節(jié)因子。ALDH1B1 調(diào)控基因的表達,包括PTEN、CTNNB1(β-catenin) 和 CSC 相關(guān)的 β-catenin 靶基因受 AMBRA1 的反向調(diào)控,表明 AMBRA1 在 ALDH1B1 調(diào)控基因的表達中具有負調(diào)控作用。我們發(fā)現(xiàn) ALDH1B1 的 K27 和 K33 連接的泛素化是通過 AMBRA1 與其他 E3 連接酶(如 TRAF6)的合作介導的。重要的是,泛素化位點映射顯示 K506、K511 和 K515 對 K27 連接的 ALDH1B1 泛素化很重要,而 K33 連接的泛素化發(fā)生在 K506。ALDH1B1 泛素化缺陷突變體增加了 ALDH1B1 的自締合能力,表明 ALDH1B1 的泛素化和自締合之間呈負相關(guān)。總之,我們的研究結(jié)果表明 ALDH1B1 受到 AMBRA1 介導的非經(jīng)典泛素化的負調(diào)控。

10層細胞工廠
Activating molecule in Beclin-1-regulated autophagy (AMBRA1) is a highly intrinsically disordered protein. As with other intrinsically disordered proteins [1], AMBRA1 is involved in various biological processes and regulates protein–protein interactions [2]. AMBRA1 is involved in the induction of autophagy via interactions with ULK1 [3] and elongin B [4] and in the induction of mitophagy via interactions with PARKIN [5] and LC3 [6]. Furthermore, AMBRA1 is crucial for nervous system development in mouse embryos [7] and skeletal muscle development in zebrafish [8].
Recently, AMBRA1 has emerged as a tumor suppressor that mediates the degradation of proto-oncogene c-Myc [9] and D-type cyclins [10]. AMBRA1-deficient tumor cells were more likely to grow when injected into nude mice than wild-type tumor cells, implying a negative relationship between AMBRA1 and tumorigenesis [11]. In addition, AMBRA1 expression inversely correlates with the stemness signature in lung cancer [12]. Despite the increasing evidence of the functional role of AMBRA1 in cancer stem cell (CSC) properties, the underlying mechanisms remain unknown.
Aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDHs) are members of a superfamily of NAD(P)+-dependent enzymes and catalyze the oxidation of aldehydes to their respective acids. ALDH1B1, which is one of the ALDH isozymes, is reported to be strictly expressed in the SC compartments of normal human colon and is highly expressed in human colonic adenocarcinoma [13]. In a clinical study [14], the upregulation of ALDH1B1 was correlated with high-grade colorectal carcinoma and the presence of lymph-node metastases, implying a potential role of ALDH1B1 in carcinogenesis. The depletion of ALDH1B1 in colon cancer cells resulted in the downregulation of Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, and PI3K/Akt pathway-related genes such as CTNNB1, Akt, and Notch1 [15]. Negative regulation of ALDH1B1 by microRNA-761 in osteosarcoma cells suppresses tumor cell proliferation by regulating TGF-β signaling and cell adhesion [16]. Although several lines of evidence suggest the importance of the modification and regulation of CSC markers by ubiquitination [17], few studies have investigated the regulators modifying ALDH1B1.
According to the Biological General Repository for Interaction Datasets (thebiogrid.org, Accessed 15 December 2020), ALDH1B1 has been identified as one of the AMBRA1-interacting proteins via affinity purification-mass spectrometry analysis of Flag-AMBRA1-transfected HEK293T human embryonic kidney cells [18]. However, the biological significance of the interaction between AMBRA1 and ALDH1B1 is not yet understood. Here, for the first time, we show that AMBRA1 downregulates the self-association and enzyme activity of ALDH1B1, and subsequently regulates CSC-associated Wnt/β-catenin signaling in an ALDH1B1-dependent manner. Mechanistically, AMBRA1 controls ALDH1B1 function via the ubiquitination of ALDH1B1 with K27- and K33-linked ubiquitin chains. Further, we found that TRAF6 and DDB1, an adaptor protein of the CRL4 complex, are able to ubiquitinate ALDH1B1 in an AMBRA1-independent fashion.

血清培養(yǎng)基瓶500ml
Beclin-1 調(diào)節(jié)的自噬 (AMBRA1) 中的激活分子是一種高度內(nèi)在無序的蛋白質(zhì)。與其他本質(zhì)上無序的蛋白質(zhì) [ 1 ] 一樣,AMBRA1 參與各種生物過程并調(diào)節(jié)蛋白質(zhì)-蛋白質(zhì)相互作用 [ 2 ]。AMBRA1 通過與 ULK1 [ 3 ] 和 elongin B [ 4 ] 的相互作用參與誘導自噬,并通過與 PARKIN [ 5 ] 和 LC3 [ 6 ] 的相互作用參與誘導線粒體自噬。此外,AMBRA1 對小鼠胚胎的神經(jīng)系統(tǒng)發(fā)育 [ 7 ] 和斑馬魚的骨骼肌發(fā)育 [ 8 ]至關(guān)重要。
最近,AMBRA1 已成為介導原癌基因 c-Myc [ 9 ] 和 D 型細胞周期蛋白 [ 10 ]降解的腫瘤抑制因子。與野生型腫瘤細胞相比,AMBRA1 缺陷型腫瘤細胞在注射到裸鼠體內(nèi)時更容易生長,這意味著 AMBRA1 與腫瘤發(fā)生之間存在負相關(guān)關(guān)系 [ 11 ]。此外,AMBRA1 表達與肺癌中的干細胞特征呈負相關(guān) [ 12 ]。盡管越來越多的證據(jù)表明 AMBRA1 在癌癥干細胞 (CSC) 特性中的功能作用,但其潛在機制仍然未知。
醛脫氫酶 (ALDH) 是 NAD(P) +依賴性酶超家族的成員,可催化醛氧化為其各自的酸。據(jù)報道,ALDH1B1 是 ALDH 同工酶之一,在正常人結(jié)腸的 SC 區(qū)室中嚴格表達,在人結(jié)腸腺癌中高度表達 [ 13 ]。在一項臨床研究 [ 14 ] 中,ALDH1B1 的上調(diào)與高級別結(jié)直腸癌和淋巴結(jié)轉(zhuǎn)移的存在相關(guān),這意味著 ALDH1B1 在致癌作用中的潛在作用。結(jié)腸癌細胞中 ALDH1B1 的缺失導致 Wnt/β-catenin、Notch 和 PI3K/Akt 通路相關(guān)基因(如CTNNB1、Akt和缺口 1 [ 15 ]。骨肉瘤細胞中微小RNA-761對ALDH1B1的負調(diào)節(jié)通過調(diào)節(jié)TGF-β信號傳導和細胞粘附來抑制腫瘤細胞增殖[ 16 ]。盡管有幾條證據(jù)表明通過泛素化修飾和調(diào)節(jié) CSC 標志物的重要性 [ 17 ],但很少有研究調(diào)查調(diào)節(jié) ALDH1B1 的調(diào)節(jié)劑。

三角細胞培養(yǎng)搖瓶250ml
根據(jù)相互作用數(shù)據(jù)集的生物通用知識庫(thebiogrid.org,2020 年 12 月 15 日訪問),通過對 Flag-AMBRA1 轉(zhuǎn)染的 HEK293T 人胚胎腎細胞的親和純化質(zhì)譜分析,ALDH1B1 已被鑒定為 AMBRA1 相互作用蛋白之一[ 18]。然而,AMBRA1 和 ALDH1B1 之間相互作用的生物學意義尚不清楚。在這里,我們首次表明 AMBRA1 下調(diào) ALDH1B1 的自締合和酶活性,隨后以 ALDH1B1 依賴性方式調(diào)節(jié) CSC 相關(guān)的 Wnt/β-連環(huán)蛋白信號傳導。從機制上講,AMBRA1 通過 K27 和 K33 連接的泛素鏈泛素化 ALDH1B1 來控制 ALDH1B1 的功能。此外,我們發(fā)現(xiàn) TRAF6 和 DDB1(CRL4 復合物的銜接蛋白)能夠以不依賴 AMBRA1 的方式泛素化 ALDH1B1。







來源:MDPI https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/21/12079/htm
上一篇: 細胞工廠使用的具體操作步驟